Comprehensive Guide to TDS Rates in India: Updated Rate Chart
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is a critical component of the Indian tax system, ensuring timely tax collection by the government. This guide provides an updated TDS rate chart, explaining various rates applicable across different income sources, helping you understand your tax obligations and ensuring compliance with the latest regulations.




Understanding TDS: What You Need to Know
TDS is a mechanism where the payer deducts a specified percentage of tax before making a payment to the recipient. The deducted tax is then deposited with the government. TDS is applicable on various payments, including salaries, interest, rent, professional fees, and commissions, among others.
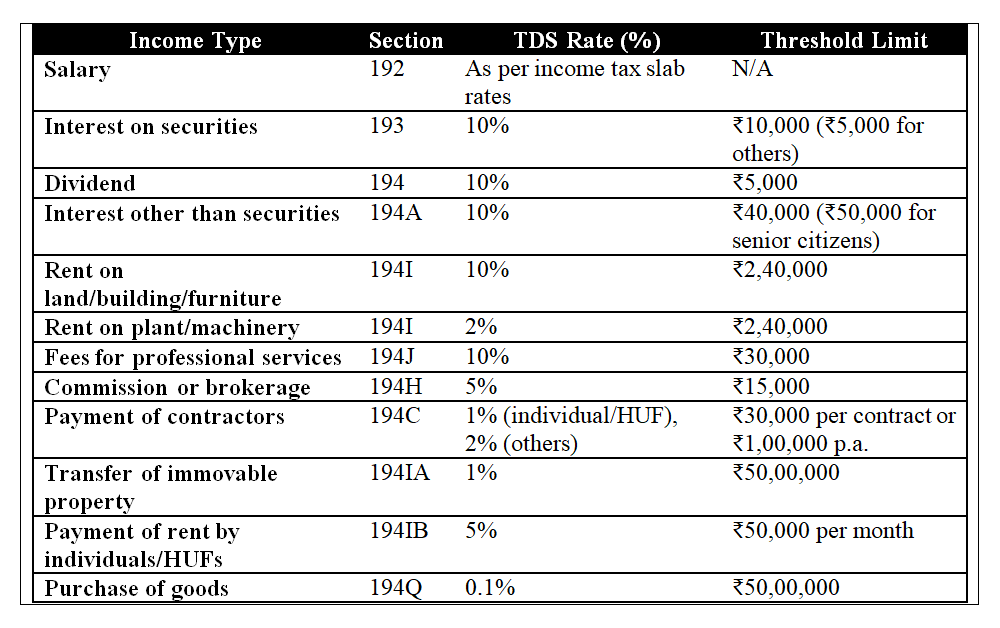
TDS Rate Chart for FY 2023-24
The following is the updated TDS rate chart for the financial year 2023-24. These rates are applicable to payments made to both resident and non-resident individuals, as well as corporate entities:



Important Points to Consider Regarding TDS
- PAN Requirement: If the payee does not provide their PAN, TDS will be deducted at the highest applicable rate or 20%, whichever is higher.
- TDS Certificate (Form 16/16A): The deductor must issue a TDS certificate to the deductee, providing details of the tax deducted and deposited with the government.
- Quarterly TDS Return Filing: Deductors must file quarterly TDS returns to report the tax deducted during the quarter.
- Impact of Not Deducting TDS: Failure to deduct or deposit TDS can result in penalties, interest, and disallowance of expenses.
How to Calculate TDS on Salary
To calculate TDS on salary, employers need to consider the total income of the employee, applicable deductions, and exemptions. The TDS is then deducted as per the income tax slab rates applicable to the employee’s income.
Exemptions and Deductions Affecting TDS
Certain exemptions and deductions can reduce the TDS amount:
- Section 80C: Investments in PPF, NSC, life insurance premiums, etc.
- Section 80D: Health insurance premiums.
- House Rent Allowance (HRA): Applicable if rent is paid and certain conditions are met.
- Leave Travel Allowance (LTA): Available for travel expenses under specific conditions.
Filing TDS Returns and Claiming Refunds
After TDS is deducted, the deductor must file TDS returns on time. The deductee can claim a refund if excess TDS has been deducted by filing their income tax return (ITR) and providing proof of the deduction through Form 16/16A.
Conclusion
Understanding TDS rates and compliance requirements is crucial for both deductors and deductees. By staying informed about the latest TDS rates and ensuring timely filing of returns, you can avoid penalties and make the most of available deductions. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource to help you navigate the complexities of TDS and stay compliant with Indian tax laws.